Everything you need to know about CAPD
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) is a type of peritoneal dialysis (PD) that uses gravity to “exchange” your used dialysis solution for fresh solution.
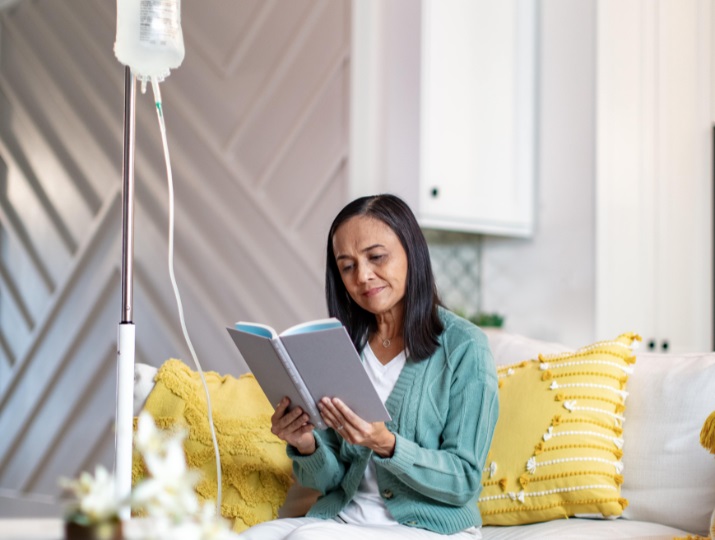

What is CAPD?
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) uses the lining of your abdomen (also known as the peritoneum) as a natural filter to remove toxins from your blood.1 There are 2 types of Peritoneal Dialysis: Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) and Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD).
CAPD does not require a machine and can be carried out in any clean place. So, whether you’re at home, work, or even travelling, you can continue with your CAPD at your convenience.
How is CAPD Done at Home?
A bag of clean dialysis solution will be connected to a soft plastic tube (known as a catheter) in your abdomen. CAPD begins when the used solution in your abdomen (known as effluent) is “exchanged” with fresh solution.
The new solution bag is hung on an IV pole, allowing gravity to draw the fresh solution into your abdomen. Once completed, the system is disconnected, and a cap is placed on your catheter so you’re free to go about your day until your next exchange. Each exchange lasts about 20–40 minutes and usually happens between 3–4 times a day, depending on your dialysis requirements.
Live Empowered with CAPD
Peritoneal dialysis provided him with a bridge to kidney transplant that he needs.
What are the benefits of CAPD?
Greater independence2
CAPD equipment is more portable than other dialysis equipment, so you can perform dialysis even when travelling. You can carry out CAPD in different places like in the workplace or at home.
Reduced physical stress 3
CAPD is known as a “continuous” therapy, which means that waste products and excess fluid can be controlled more easily during the treatment process, which is less taxing on the heart and blood vessels.
Less prescriptions
CAPD patients may also be able to take fewer medications and supplements than if undergoing Haemodialysis (HD).
Longer lasting residual kidney function4
Patients on PD might retain kidney function longer than people under HD.
A less restricted diet5
A balanced diet is key for all CKD patients, but since PD is carried out several times a day, there is less time for waste to accumulate in your body compared to HD, which means that you can eat more of the foods you enjoy. Additionally, daily PD means that potassium removal is more efficient than HD, so PD patients don’t have to monitor their potassium intake as closely as HD patients.
FAQ
Where to go next?
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) at Home
APD is a type of peritoneal dialysis, which is different from haemodialysis. We explain more on PD.
In-Centre Haemodialysis (In-Centre HD)
You may prefer to receive dialysis at a hospital or treatment centre near you with ICHD.
Kidney Transplant
A kidney transplant may be a treatment option for some patients, while supportive care without dialysis might be suitable for others.
