All About Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) is a home therapy option for end-stage kidney disease, performed using a dialysis machine, which helps to deliver and drain the dialysate automatically.

What is Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)?
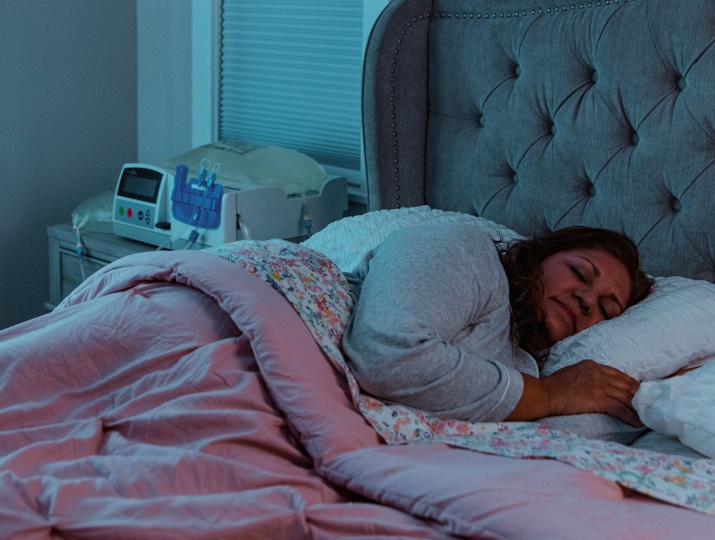
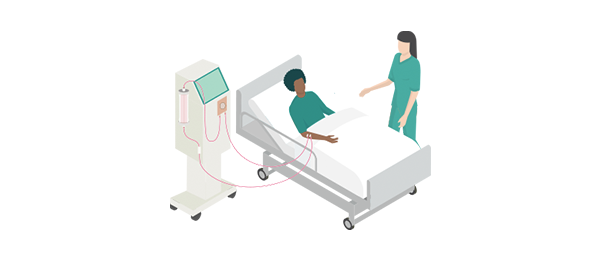
Automated PD (APD) is a type of PD that is performed using a dialysis machine, which helps to deliver and drain the dialysate automatically, with minimal human intervention. This dialysis machine, also called a cycler, is programmed to provide the exact amount of dialysis prescribed by your clinician. An APD exchange typically takes between 8 and 12 hours and can be performed overnight while you sleep.
How does Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) work?
Before each dialysis session, your APD cycler is connected to 10-15 liters of clean dialysis solution. A tube from the cycler is then connected to a catheter in your abdomen. The APD cycler is programmed to control the movement of clean dialysis solution into your abdomen by the machine.
It drains the used dialysis solution from your body and replaces it with fresh solution at regular intervals throughout the therapy duration. You will have to set up the dialysis machine with fresh equipment and dialysis fluid for each APD session. Every patient is different and your APD cycler’s program will be customized to your specific needs.
Live Empowered with Automated Peritoneal Dialysis
Automated peritoneal dialysis allows him to live the life he wants.
Why do I need APD?
Lower chances of swelling due to excess fluid in your body1
Ultrafiltration is the removal of fluid from the patient body, and it is one of the kidney functions that dialysis treatment replaces. Peritoneal dialysis (PD) uses ultrafiltration to remove fluid via the peritoneal membrane. APD can have a better ultrafiltration effect in some patients, allowing for more fluid to be removed during each exchange, thus reducing swelling due to excess fluid.
Potentially lower risk of peritonitis 1
APD exchange is usually done overnight, therefore patients would only need to connect and disconnect their catheter to the APD machine once a day. Whereas, CAPD exchanges are usually done 3-4 times during the day, patients would then need to connect and disconnect their catheter to the dialysate bags multiple times a day, which can significantly increase their risk of infection.
Less discomfort2
CAPD exchanges are usually done with patients in a sitting position, while APD exchanges are usually done with patients in their lying position. Therefore, the pressure felt in your abdomen during APD could be 50% lower compared to CAPD.
Greater daytime flexibility2
As APD is performed during sleep, you can enjoy more flexibility during the day. In fact, over 60% of APD patients are employed full-time, so you can still support yourself and your family financially while on APD.
Despite having a lower risk of complications for APD patients, general PD complications may still arise, such as infection and hernia.
Learn more about PD’s complications and side effects.
FAQ

Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
CAPD can be performed at work, home or during travel.
In-Centre Haemodialysis (In-Centre HD)
You may prefer to receive dialysis at a hospital or treatment centre near you with ICHD.
Kidney Transplant
A kidney transplant may be a treatment option for some patients, while supportive care without dialysis might be suitable for others.
